Nearly 65% of women of reproductive age in the United States use some form of contraception, underscoring the widespread need for reliable birth control options. With so many individuals depending on contraceptives, understanding the full range of methods and their proper administration is essential for both healthcare providers and patients alike.
Among these options, Depo-Provera (or the Depo shot) stands out as a long-acting injectable form of birth control. Administered every three months, it offers a convenient, low-maintenance alternative to daily or weekly contraceptives, making it a popular choice for many.
This article will walk you through the correct technique for giving a Depo shot, including preparation, administration, aftercare, and key safety considerations, ensuring both proper use and patient safety.
Key Takeaways
- Depo-Provera is an injectable form of birth control, administered every three months to provide effective contraceptive protection.
- It is injected into the gluteal or deltoid muscle using a 22-gauge, 1½-inch needle for deep intramuscular use.
- The Depo-SubQ Provera 104 alternative offers a subcutaneous injection with a smaller needle and lower volume.
- It is less painful and is a more straightforward method for self-injection with proper training.
- Proper preparation and storage are crucial to maintaining the medication’s effectiveness. Depo-Provera should be stored at room temperature and shaken well before use. Avoid extreme temperatures or freezing.
- Documentation and follow-up are essential for maintaining the effectiveness of Depo-Provera.
- Providers must track injection details, patient responses, and follow-up appointments for timely administration.
- Side effects can include changes in menstrual cycles. Healthcare providers should offer counseling on potential outcomes and recommend monitoring bone health for individuals who use these medications for an extended period.
About: Medical Spa RX provides medical practices with premium products at the best prices. If you’re looking to buy Depo-Provera online for your practice, the sales representatives at Medical Spa RX can give you guidance.
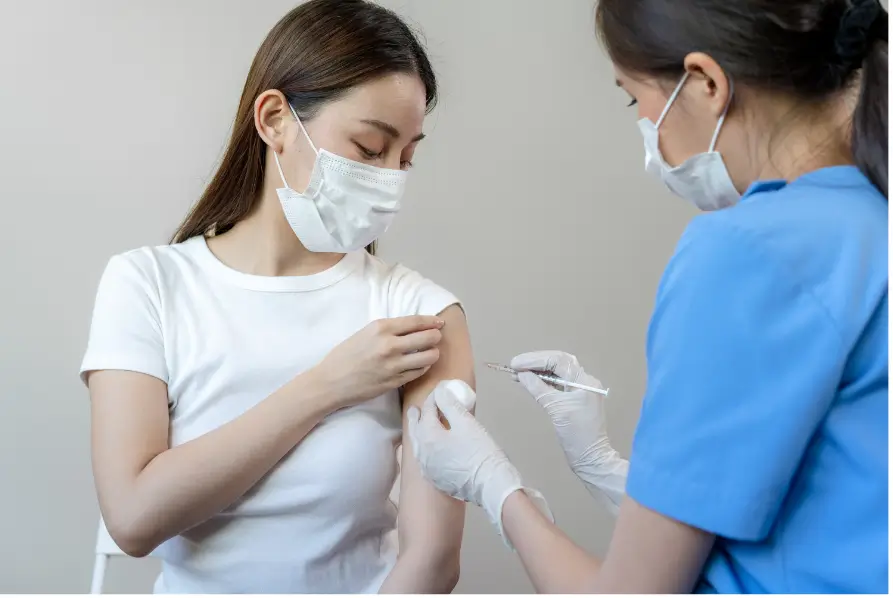
Intramuscular Depo-Provera Injection: Dose, Needle, and Site
The Depo-Provera intramuscular injection is administered deep into the gluteal or deltoid muscle, ensuring effective absorption of the 150 mg dose for three months of contraceptive protection. Proper needle selection is crucial for achieving accurate placement. For patients with a larger body habitus, a longer needle may be required to ensure the injection reaches deep muscle tissue, avoiding the subcutaneous tissue, which could reduce effectiveness.
Rotating injection sites is also recommended to minimize discomfort and prevent tissue irritation. The following points outline the key steps for intramuscular use:
- Dose: Administer 150 mg every 3 months (13 weeks).
- Needle: Use a 22-gauge, 1½-inch needle to ensure the injection reaches deep muscle tissue.
- Injection Site: The recommended sites are the gluteal (buttock) or deltoid (upper arm) muscles.
- Technique: Use deep intramuscular injection with strict aseptic precautions to prevent infection.
- Formulation: Available as a 1 mL vial or prefilled syringe; shake vigorously before use.
- Site Rotation: Alternate injection sites with each dose to reduce tissue irritation and promote comfort.
- Pregnancy Screening: Administer the injection within the first 5 days of the menstrual cycle or postpartum to rule out pregnancy.
- Scheduling: Maintain the recommended schedule to ensure continuous contraceptive coverage and effectiveness.
How long does it take for the Depo shot to work? The Depo shot typically begins to work within 24 hours when administered during the first 5 days of a menstrual cycle. If administered at any other time, it may take up to 7 days to provide complete contraceptive protection.
Subcutaneous Depo-Provera: Alternative Protocol and Technique
The Depo-SubQ Provera 104 injection is a subcutaneous alternative that delivers 104 mg of medroxyprogesterone acetate (the generic name for Depo-Provera) for three months of contraceptive protection. This version uses a smaller needle and less volume than the intramuscular formulation, making it a less painful option for some users. Proper technique is still critical to ensure reliable absorption and continued effectiveness. Key administration points include:
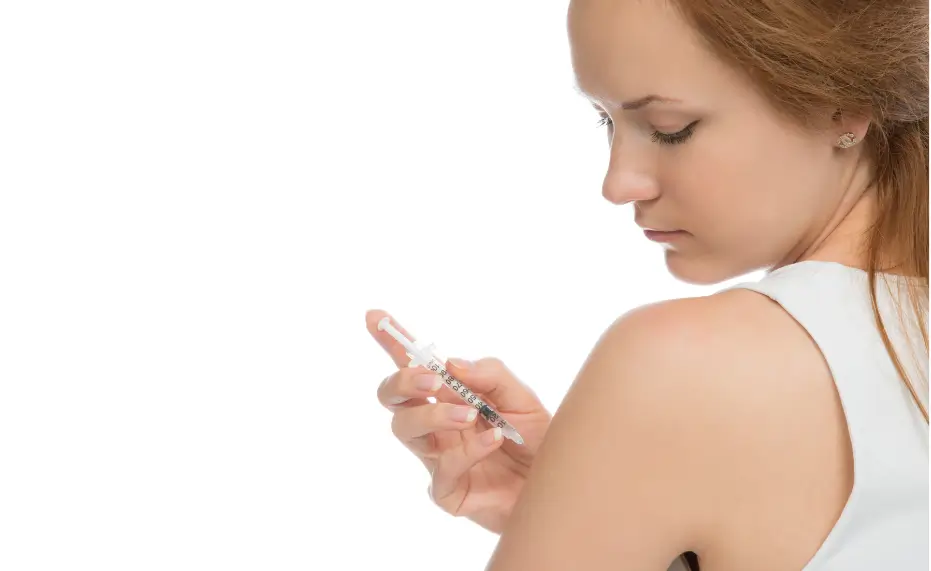

- Dose: 104 mg every 3 months (13 weeks).
- Needle: Use a 26-gauge, 3/8-inch needle for subcutaneous injection.
- Injection Site: Preferred sites are the upper thigh or lower abdomen (avoid the navel and waistline).
- Technique: Pinch the skin and insert the needle at a 45-degree angle into the subcutaneous tissue.
- Injection Time: Inject the solution slowly over 5–7 seconds to allow the medication to be absorbed fully.
- Post-Injection: Apply gentle pressure to the site; dispose of the needle in a sharps container following proper guidelines.
- Self-Injection: Although U.S. guidelines recommend that a healthcare professional administer the injection, self-injection is widely used internationally and has been shown to improve access to contraception for many individuals.
- Benefits: This method is less invasive, easier to administer, and more suitable for at-home use with proper training.
Preparing and Storing Depo-Provera for Safe Administration
Proper preparation and storage of Depo-Provera are crucial to ensure the medication’s effectiveness and safety. The injectable suspension should be stored upright at controlled room temperature (between 20° to 25°C / 68° to 77°F) to maintain its integrity. Before use, shake the vial well to ensure that the medication is evenly mixed.
Always use sterile syringes and needles to administer the injection. For the intramuscular injection, ensure that the needle is long enough to reach deep into the muscle. When administering the subcutaneous version, a smaller needle and a shallower injection depth are appropriate. Never freeze the medication or expose it to extreme temperatures, as this can affect potency.
Following proper disposal and handling protocols is vital to prevent contamination and maintain a sterile environment during administration. By adhering to these best practices, healthcare providers can ensure that the medication remains safe and effective for patients receiving Depo-Provera injections.
Documentation and Follow-Up After Depo-Provera Injection
Thorough documentation and follow-up visits are essential to ensure the safe and effective use of Depo-Provera. Healthcare providers must record each injection, monitor patient responses, and address any complications that arise. The key steps in this process include:

- Injection Details: Document the date, dosage, and injection site to maintain accurate records.
- Patient History: Note any side effects or concerns reported by the patient during the injection process.
- Next Appointment: Schedule the next injection appointment within 12-14 weeks to maintain contraceptive effectiveness.
- Counseling: Provide guidance on potential side effects, including changes in menstrual cycles and other common concerns.
- Emergency Contraception: Advise patients to use backup methods if they miss an injection.
- Bone Health Monitoring: Track the long-term effects of Depo-Provera on bone density, as prolonged use may impact bone health.
- Pregnancy Testing: If a patient misses an injection and has unprotected sex, they must immediately test for pregnancy.
Regular follow-ups and proper documentation ensure that Depo-Provera remains an effective and safe form of contraception.
Conclusion
Administering Depo-Provera requires careful attention to technique, proper needle selection, and consistent scheduling to ensure its effectiveness. Correctly storing the medication and adhering to safety protocols are equally crucial for maintaining the integrity of the drug.
Patient education about potential side effects, the importance of timely injections, and follow-up visits plays a critical role in ensuring successful contraceptive outcomes. By following best practices and maintaining thorough documentation, healthcare providers can ensure accurate and reliable Depo-Provera administration, delivering effective contraceptive care for patients.
FAQs
1. What is Depo-Provera and how does it work?
Depo-Provera is a hormonal contraceptive injection containing medroxyprogesterone acetate, which prevents ovulation and thickens cervical mucus to reduce the chance of pregnancy.
2. How often do I need to get the Depo-Provera shot?
Get the injection every three months (12–13 weeks) for continuous contraceptive protection.
3. What are the common side effects of Depo-Provera?
Common side effects include changes in menstrual bleeding, weight gain, headaches, and delayed return to fertility after discontinuation.
4. Can I administer Depo-Provera at home?
Subcutaneous Depo-Provera can be self-injected at home in some regions, but in the U.S., this is considered off-label and should be discussed with your healthcare provider.
5. What should I do if I miss a scheduled Depo-Provera shot?
If more than 15 weeks have passed since your last injection, you may need a pregnancy test before the next dose, and consider using backup contraception for seven days.
6. Is Depo-Provera safe for long-term use?
Experts do not recommend using Depo-Provera beyond two years due to potential effects on bone mineral density, unless other contraceptive options are unsuitable.
7. How should I store Depo-Provera at home?
Store Depo-Provera at room temperature (below 30°C/86°F), away from heat, moisture, and direct sunlight. Do not refrigerate or freeze the medication.
References
Daniels K, Abma JC. Current Contraceptive Status Among Women Aged 15–49: United States, 2017–2019. NCHS Data Brief, no 388. Hyattsville, MD: National Center for Health Statistics. 2020. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/databriefs/db388-H.pdf
Contraceptive Use in the United States. Guttmacher Institute. Updated June 2023. https://www.guttmacher.org/fact-sheet/contraceptive-use-united-states
Depo-Provera (birth control shot). Mayo Clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/depo-provera/about/pac-20392204