When it comes to cosmetic injectables—especially those designed for skin rejuvenation and wrinkle reduction—FDA approval isn’t just a regulatory milestone; it’s a critical marker of safety, efficacy, and quality control. For both practitioners and patients, this stamp of approval signifies that a product has undergone rigorous scientific scrutiny, making it more trustworthy and often more accessible in the U.S. market.
This distinction becomes even more critical when evaluating injectable neuromodulators like Innotox, a formulation of botulinum toxin. Unlike traditional cosmetic products, these treatments are regulated as drugs, not cosmetics, which elevates the importance of their regulatory status. Without FDA approval, a product may face limited market access and hesitancy among healthcare providers, regardless of its popularity elsewhere.
In this article, we’ll break down the current FDA approval status of Innotox, explore what this means for consumers and professionals, and compare it to other botulinum-based treatments already on the market.
Key Takeaways
- Innotox is a ready-to-use liquid botulinum toxin originally developed and approved for cosmetic use in South Korea.
- While approved in South Korea, Innotox does not have FDA approval and cannot be marketed for general use in the U.S.
- Clinical trials are ongoing, but Innotox has not yet received formal FDA approval for safety and effectiveness in the U.S.
- Some U.S. providers import or use Innotox off-label, but this carries legal risks and lacks FDA quality assurance.
- U.S. practitioners using Innotox must fully disclose its non-FDA status and obtain informed consent from patients.
About: Medical Spa RX provides medical practices with premium products at the best prices. If you’re looking to buy Innotox online for your practice, the sales representatives at Medical Spa RX can give you guidance.
Regulatory Status: Innotox in South Korea vs FDA/EMA
Innotox, developed by Medytox Inc., became the first-ever ready-to-use liquid botulinum toxin type A, approved by South Korea’s Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS) in 2013. This advancement has created a new standard in the aesthetic industry by eliminating the need for reconstitution, offering improved accuracy and efficiency compared to traditional powdered products like Botox and Dysport.

While Innotox has found success in South Korea and other non-U.S. markets, it has yet to gain approval from the FDA or the EMA. Without such approvals, the toxin cannot be marketed or legally used for general treatment in these regions. FDA clearance is a lengthy process that requires significant trials.
To date, Medytox has not filed a Biologics License Application (BLA) or an Investigational New Drug (IND) application with the FDA, unlike some of its competitors. Therefore, the accessibility of Innotox in Western markets remains limited, and it may be a while before its use becomes widespread in the U.S.
Clinical Trials & FDA Submissions for Innotox
In order for any product to be approved by the FDA, it must undergo a rigorous clinical trial process to confirm safety and efficacy. Innotox is currently navigating this process, which involves several key phases:
- Preclinical Research: Safety testing in laboratory settings
- Phase I Trials: Small groups of participants to assess basic safety
- Phase II Trials: Focus on efficacy, side effects, and optimal dosage
- Phase III Trials: Large-scale studies comparing Innotox to existing treatments
- FDA Review: Submission of a Biologics License Application (BLA)
While Medytox has submitted data to the FDA, no public record exists of an FDA-filed IND or BLA for Innotox. Without formal U.S. trial phases or FDA submission announcements, the approval timeline for Innotox in the U.S. is uncertain.
Practitioners should keep an eye on Medytox’s developments as ongoing trials may affect the future availability of Innotox in the U.S.
Imported/Off‑Label Use of Innotox in the U.S.
Despite Innotox not being approved by the FDA, it has been imported and used off-label by some aesthetic practitioners, typically in specialized clinics or medical spas. However, it’s important to understand that using an unapproved product outside its labeled indications is legally and ethically complex. The off-label use of Innotox falls under personal-use exemptions or may occur via unofficial import channels.
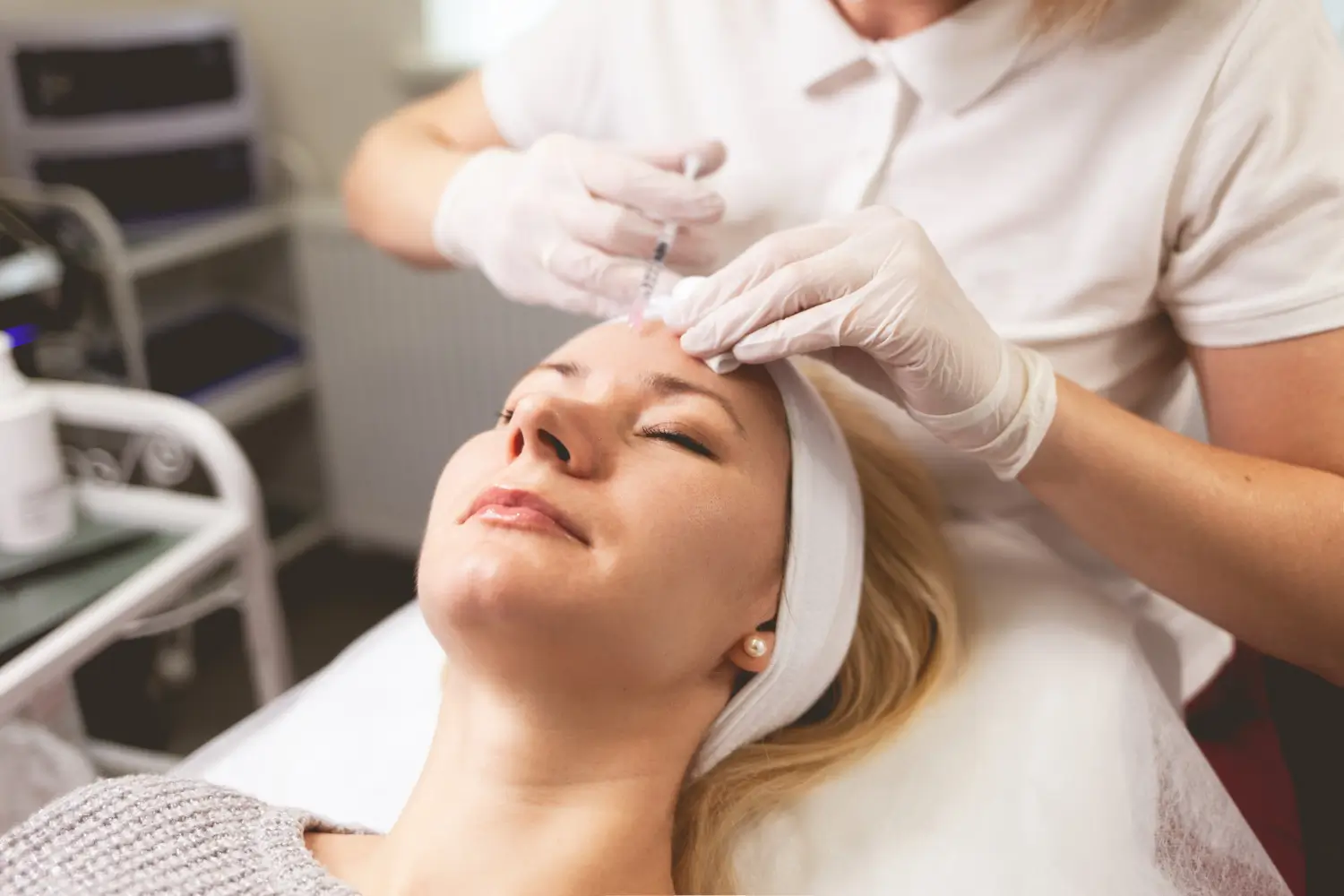
Risks of Off-Label Innotox Use
- Lack of FDA oversight on quality, storage, or efficacy
- Potential safety concerns due to insufficient regulated testing
- Increased risk of counterfeit products
- No official recourse in case of adverse events
Although Innotox before and after results can be impressive, off-label use carries significant risks and legal implications for both the patient and practitioner. Practitioners must consider these aspects carefully before proceeding with any treatments.
Legal Implications & Practitioner Disclosure for Innotox
Practitioners using Innotox in the U.S. must adhere to both legal and ethical responsibilities. Transparency regarding the risks, side effects, and expected outcomes of using an unapproved product is essential to ensure informed consent. Legal obligations also extend to patient confidentiality, accurate documentation, and adherence to professional standards.
As of now, the FDA has not granted approval to Innotox, and its use remains limited. Only licensed professionals with appropriate training in botulinum toxin procedures should administer Innotox, ensuring compliance with medical regulations and safeguarding patient safety. Practitioners should maintain high levels of accountability and clarity when using Innotox off-label, making sure that patients are fully informed of its regulatory status.
Conclusion
Innotox is a promising botulinum toxin with a unique formulation and significant potential for use in both cosmetic and therapeutic treatments. Although it is currently FDA-approved and accessible in the U.S., it remains widely used in South Korea and other markets, with strong support from practitioners globally.
As Medytox navigates clinical trials and the FDA approval process, Innotox may eventually enter the U.S. aesthetic market, offering a ready-to-use alternative to traditional botulinum toxins.
Until then, practitioners should be cautious with its off-label use, ensuring they comply with legal and ethical requirements. Patients and practitioners alike should remain informed about Innotox’s regulatory status and its potential risks, awaiting the product’s official clearance for wider use.
FAQs
1. What is Innotox?
Innotox is a liquid botulinum toxin type A developed by Medytox. It is designed for cosmetic wrinkle reduction and similar therapeutic applications.
2. Is Innotox FDA approved in the U.S.?
No. Innotox has not yet received FDA approval for use in the United States.
3. Can U.S. clinics legally use Innotox?
Only under very specific exemptions or personal use allowances. Commercial sale or promotion is not allowed without FDA approval.
4. Why do some providers still use Innotox in the U.S.?
Some practitioners may use imported Innotox off-label, often drawn by its pre-mixed format, but this is not without risk or legal responsibility.
5. What are the risks of using non-FDA approved Innotox?
Potential risks include uncertain product quality, inadequate FDA oversight, counterfeit concerns, and potential legal consequences for the provider.
6. How is Innotox different from Botox?
Innotox is a ready-to-use liquid formulation, while Botox is a freeze-dried powder that requires reconstitution before use.
7. Is Innotox available in Europe?
As of now, Innotox is not EMA-approved either. It remains primarily available in South Korea and other markets where it has secured local approval.
References
Bonalanza B. Injectable Skin Boosters: The Science Behind this New FDA-Approved Injectable Category. Next Steps in Dermatology. Published February 27, 2024. https://nextstepsinderm.com/derm-topics/injectable-skin-boosters-the-science-behind-this-new-fda-approved-injectable-category/
Cosmetics and Your Health: NIEHS Research Findings. https://www.niehs.nih.gov/sites/default/files/Cosmetics_and_Your_Health_fact_sheet_Jan2024_508.pdf
Nigam P, Nigam A. BOTULINUM TOXIN. Indian Journal of Dermatology. 2010;55(1):8. doi:https://doi.org/10.4103/0019-5154.60343





















