Vision is among the most vital human senses, enabling individuals to interact with their environment and perform daily activities effectively. According to the World Health Organization, over 2.2 billion people worldwide experience some form of vision impairment or blindness, many of which are preventable or treatable with timely intervention. Advances in eye care and medical treatments play a critical role in preserving sight and enhancing quality of life, particularly for those affected by complex retinal diseases.
One such advancement is Vabysmo, a novel therapy specifically designed to manage retinal conditions. However, the success of this treatment depends heavily on the precise administration technique used by healthcare providers. Proper handling and delivery of Vabysmo not only maximizes therapeutic effectiveness but also minimizes potential complications, directly influencing patient outcomes.
This article will delve into the Vabysmo administration technique, outlining best practices, essential safety protocols, and key considerations to assist healthcare professionals in delivering optimal care.
Key Takeaways
- Proper preparation of Vabysmo with the vial or prefilled syringe is essential. Use sterile gloves and aseptic technique to avoid contamination.
- Minimize the time between preparation and injection to maintain drug stability and reduce infection risk.
- Administer injections 3.5–4.0 mm posterior to the limbus using a 30-gauge needle, avoiding the horizontal meridian to protect the lens and optic nerve.
- Use topical anesthesia and antiseptic (e.g., povidone-iodine) before injection to reduce patient discomfort and infection.
- Monitor patients immediately after injection for side effects such as intraocular pressure spikes, redness, irritation, or bleeding.
- Educate patients to report symptoms like vision changes, pain, floaters, or redness promptly to catch complications early.
- Store Vabysmo refrigerated at 2°C to 8°C, protected from light; do not freeze under any circumstances.
- If necessary, the medication can be kept at room temperature (up to 25°C) for up to 24 hours but should never be returned to refrigeration.
- Ensure cold-chain compliance during transport using insulated packaging and monitor temperature to maintain medication integrity.
- Staff training on handling, storage, and administration protocols is vital to reduce errors and optimize clinical outcomes.
- Regular audits and updates of clinical protocols help maintain high standards of care and patient safety.
- Following these guidelines helps clinicians maximize Vabysmo’s therapeutic benefits, reduce treatment burden, and improve patient quality of life.
About: Medical Spa RX provides medical practices with premium products at the best prices. If you’re looking to buy Vabysmo online for your practice, the sales representatives at Medical Spa RX can give you guidance.
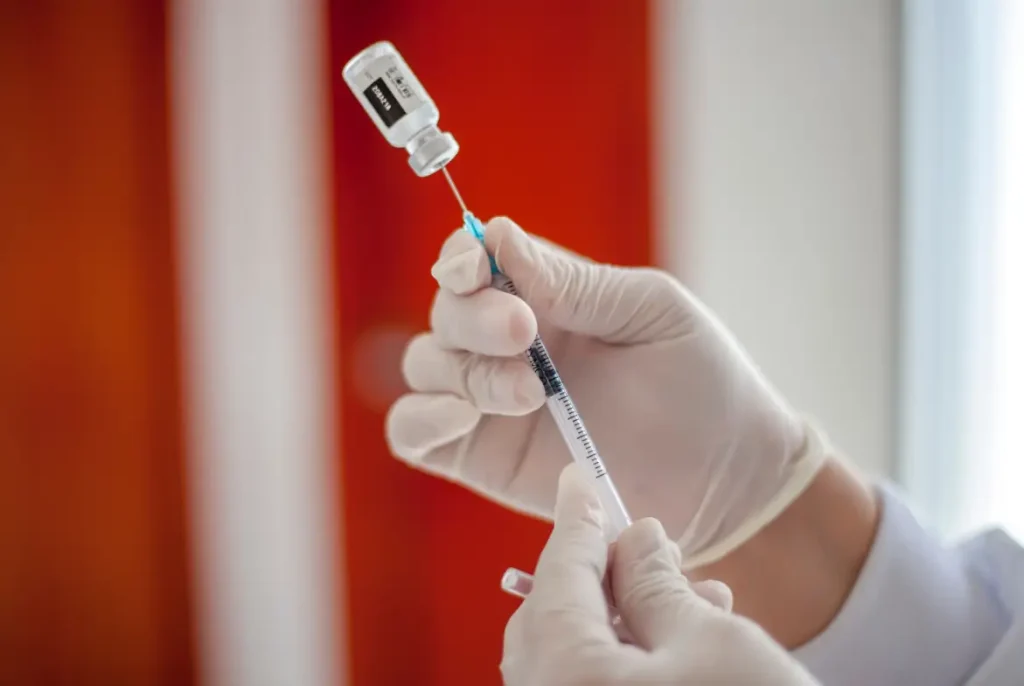
Vabysmo Preparation: Vial and Prefilled Syringe Safety Handling
Proper preparation of Vabysmo is critical to ensure safe and effective intravitreal injection. Vabysmo is available as a single-dose vial or a prefilled syringe, both containing 6.0 mg of faricimab in 0.05 mL of solution. For the vial presentation, clinicians must withdraw the dose using a 19-gauge filter needle to ensure sterility and remove particulates, then switch to a 30-gauge injection needle before administering.
For the prefilled syringe, avoid tapping or shaking it to prevent air bubbles or destabilization of the solution. Then, do the following:
- Hold the syringe upright to allow any bubbles to rise and expel them gently.
- Adjust the dose by aligning the plunger with the appropriate mark on the syringe.
- Always inspect the solution for particulates or discoloration before use.
- Use sterile gloves and prepare the medication in a clean area.
Minimizing preparation time reduces the risk of contamination, which is an essential part of patient safety information.
Injection Technique: Dose, Equipment, and Site Selection
Vabysmo treatment is administered via intravitreal injection under strict aseptic technique. The recommended dose is 6.0 mg (0.05 mL). Use a 30-gauge needle, typically ½ inch long, to minimize tissue trauma. The injection is performed approximately 3.5–4.0 mm posterior to the limbus into the vitreous cavity, carefully avoiding the horizontal meridian to reduce the risk of injury to the lens or optic nerve.
Prior to injection, apply topical anesthesia and an antiseptic such as povidone-iodine to minimize discomfort and infection risk. Stabilize the eye to prevent sudden movements and insert the needle perpendicular to the sclera. Inject the solution slowly to ensure even dispersion, and then gently withdraw the needle. If reflux occurs, apply gentle pressure with a sterile cotton tip to reduce medication loss.
Post-Injection Monitoring and Complication Prevention
Following Vabysmo administration, patients should be closely monitored for immediate complications, including increased intraocular pressure (IOP), endophthalmitis, or retinal detachment. It is standard practice to measure IOP within 30 minutes post-injection, especially in patients with a history of glaucoma or ocular hypertension.

Patients must be educated to report symptoms such as eye pain, changes in vision, floaters, or redness, as these may indicate delayed complications that require urgent evaluation. Verbal and written aftercare instructions are essential for reinforcing symptom recognition and proper eye care following injection. While prophylactic topical antibiotics are sometimes used, their routine application is debated and generally reserved for specific clinical indications.
Common Post-injection Concerns
Clinicians should remain vigilant for several side effects following intravitreal injection of Vabysmo, many of which are similar to those seen with safother anti-VEGF agents such as Avastin. In the ongoing discussion of Vabysmo vs Avastin, it is important to note that most adverse events associated with Vabysmo are mild and transient.
A transient intraocular pressure spike is common immediately after injection but usually resolves within 30 to 60 minutes. Patients may experience mild eye irritation, including itching or discomfort, which typically subsides within one to two days. Subconjunctival hemorrhage can occur due to a minor blood vessel rupture during the injection, presenting as a red spot on the sclera that resolves spontaneously.
More severe complications, such as endophthalmiti,s are rare but require immediate medical intervention. Early detection through patient education and timely follow-up is critical in managing risks and maintaining treatment safety.
Storage, Transport, and Compliance With Vabysmo Handling Guidelines
Maintaining Vabysmo’s sterility and efficacy depends on proper storage and transport. The medication must be kept refrigerated at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) and shielded from light until administration. It must never be frozen, as freezing compromises its integrity. When necessary, Vabysmo can be kept at room temperature (up to 25°C or 77°F) for no longer than 24 hours before use, but it cannot be returned to refrigeration afterward.

During transport, ensure temperature stability with appropriate cold-chain packaging. Always use the oldest stock first to avoid waste and ensure drug potency. Facilities should maintain a monitored cold storage system, use insulated containers for transport, and provide staff training on proper cold-chain management. Documentation of storage and handling practices is crucial for regulatory compliance and quality assurance.
Conclusion
Administering Vabysmo effectively requires strict adherence to preparation, injection, and post-procedure protocols. Following aseptic techniques, confirming correct dosing, and selecting injection sites with precision are essential for successful treatment outcomes. Monitoring patients immediately after injection allows early detection and management of complications, ensuring safety.
Furthermore, compliance with storage and transport guidelines preserves the drug’s efficacy and minimizes risks. Ongoing staff training and procedural audits enhance clinical proficiency and reduce errors. By implementing these best practices, healthcare providers can maximize the therapeutic benefits of Vabysmo, providing patients with safe and effective management of retinal diseases.
FAQs
1. What is Vabysmo used for?
Vabysmo is used to treat neovascular (wet) age-related macular degeneration and diabetic macular edema in adults.
2. How often is Vabysmo administered?
Initial injections are typically given monthly, followed by maintenance dosing every 1–4 months based on patient response.
3. What are the most common side effects of Vabysmo?
Mild eye discomfort, increased intraocular pressure, and conjunctival hemorrhage are common side effects.
4. Can Vabysmo be used with other ocular treatments?
Yes, but combinations should be evaluated carefully by a retina specialist for safety and efficacy.
5. Is Vabysmo better than other anti-VEGF treatments?
Vabysmo is comparable in efficacy and may require fewer injections over time, depending on patient response.
6. How long does it take for Vabysmo to work?
Many patients notice improvement in vision within a few weeks of starting treatment.
7. Who should not receive Vabysmo?
Patients with ocular or periocular infections, or those with hypersensitivity to any component, should not receive Vabysmo.
References
World Health Organization. Blindness and vision impairment. Published August 10, 2023. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/blindness-and-visual-impairment
Retinal Diseases: Types, Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, Outlook. Healthline. Published November 4, 2022. https://www.healthline.com/health/eye-health/retinal-diseases